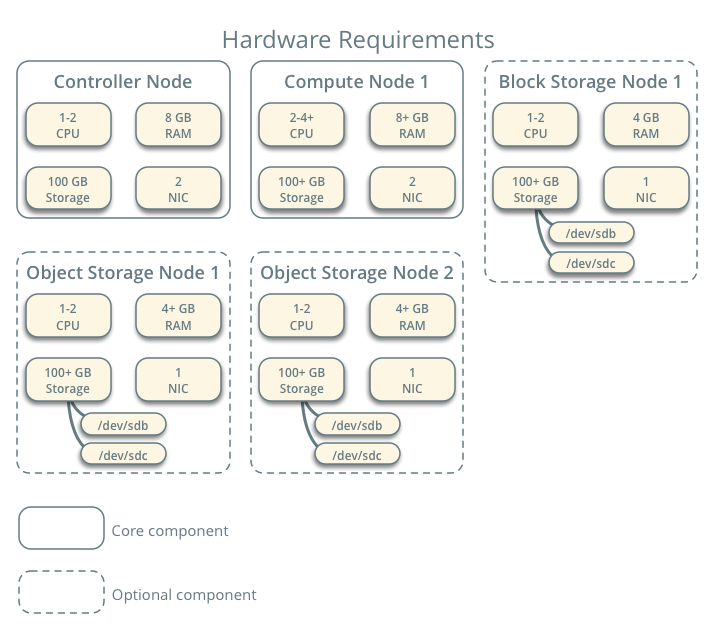
Example Architecture
The example architecture requires at least two nodes (hosts) to launch a basic
virtual machine or instance. Optional services such as Block Storage and Object Storage require
additional nodes.
Controller: The controller node runs the Identity service, Image service,
management portions of Compute, management portion of Networking, various Networking agents, and the
Dashboard. It also includes supporting services such as an SQL database, message queue, and NTP.
Optionally, the controller node runs portions of the Block Storage, Object Storage, Orchestration, and
Telemetry services. The controller node requires a minimum of two network interfaces.
Compute: The compute node runs the hypervisor portion of Compute that operates instances. By
default, Compute uses the KVM hypervisor. The compute node also runs a Networking service agent that
connects instances to virtual networks and provides firewalling services to instances via security
groups. You can deploy more than one compute node. Each node requires a minimum of two network
interfaces.
Block Storage: The optional Block Storage node contains the disks that the Block
Storage and Shared File System services provision for instances. For simplicity, service traffic between
compute nodes and this node uses the management network. Production environments should implement a
separate storage network to increase performance and security. You can deploy more than one block
storage node. Each node requires a minimum of one network interface.
Object Storage: The
optional Object Storage node contain the disks that the Object Storage service uses for storing
accounts, containers, and objects. For simplicity, service traffic between compute nodes and this node
uses the management network. Production environments should implement a separate storage network to
increase performance and security. This service requires two nodes. Each node requires a minimum of one
network interface. You can deploy more than two object storage nodes.